Runners in particular are prone to developing stress fractures in the foot. Stress fractures of the foot will also occur in other sports, but are more than likely due to training. Stress fractures of the foot are caused by repetitive loading or stress. These fractures are most common in runners or athletes who have rapidly ramped up their training schedules.
Why Do Foot Stress Fractures Occur?
Our bone has a certain density or thickness. As we age, or due to inactivity that strength diminishes. In addition, our bone will gain density or strength if we exercise. If we start running the bone will sense whether or not it is thick enough to deal with the repetitive stress. If you build up your training slowly, the bone will adapt and become thicker or more dense. But this process takes time. If you progress your training too rapidly, then the amount of stress you put on your foot will increase, and the bone may start to break internally. Inside the hard outer shell of the bone is a latticework of finer spicules of bone. That is where stress fractures first appear.
4 Common Foot Stress Fractures:
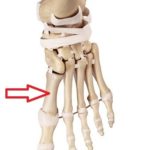
Metatarsal stress fractures of the foot: The metatarsals are the longest bones in the foot. There are 5 metatarsals, one for each toe. Stress fractures can occur in any of the metatarsals. If you have localized severe tenderness and/or swelling over your metatarsals, you likely have a stress fracture. Most metatarsal stress fractures will heal without the need for surgery. Some metatarsal fractures might simply require a boot as seen here. Stress fractures of the inner or first metatarsal and the most outer or fifth metatarsal can be trickier to manage and usually require that you use crutches to allow for healing. For metatarsal fractures that do not heal surgery might be necessary.
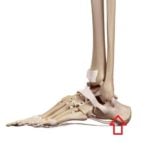
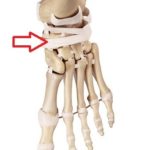
Stress fracture of the navicular : Stress fractures of the navicular are the most ominous of the stress fractures that can occur in the foot. The pain from a navicular stress fracture is on the upper or inner side of the middle of your foot. Once this fracture is suspected it is critical that you see your doctor. A navicular stress fracture that doesn’t heal will end an athletes or a runners career very quickly. This is a controversial topic, but the classic literature shows that these fractures do not usually require surgery. If you are told you might need surgery for this make sure you see an Orthopedic Surgeon with specific Foot and Ankle training. This is a very tricky procedure.
Stress fracture of the sesamoids. Sesamoids are little bones the size of a bean that sit under your big toe. Pain underneath your big toe could signify a sesamoid stress fracture. It could also mean that the sesamoids are just a little upset, but not fractured. Often an MRI might be needed to tell the difference. If you are unable to run because of pain underneath your big toe and it does not go away with rest or a few weeks in a boot then consider seeing your doctor before running again.
Do I Have A Stress Fracture In My Foot?
If you have persistent pain in your foot that is very localized to a particular location then it is possible that you have a stress fracture in your foot. If a short period of activity modification doesn’t help improve the pain then you should see your Orthopedic Surgeon. As mentioned above, if you feel you might have a stress fracture of the navicular you should see your surgeon sooner rather than later.
Treatment of Foot Stress Fractures
Most stress fractures in your foot will respond to activity modification. Some stress fractures may require a boot or a cast, and others may require that you are on crutches for a while. If you suspect that you may have a stress fracture in your foot it is a good idea to see your Orthopedist.
Recovery From Stress Fractures In The Foot
The recovery from most stress fractures in the foot is generally very straightforward. The fractures will usually heal within a few weeks and most athletes can return to the field in 6-12 weeks, depending on the fracture and its location. Surgery is very rarely needed for stress fractures of the foot.