A broken tibia is not common in sports. But a tibia fracture can be a very severe and very painful injury that must be managed correctly if the athlete wishes to return to sports. Those of us who are older enough to remember can recall exactly where we were when we saw LT cause Joe Theismann’s tibia fracture. Tibia fractures are less common than soft tissue or ligament injuries in sports, but they do occur. Up to 92% of athletes can expect to recover from their tibia fracture and return to sports.
Tibia fractures can occur in athletes who participate in contact sports such as football, soccer and rugby. These fractures are far more common in high energy injuries such as car accidents or if a bicyclist is hit by a car. In sports, most tibia fractures occur due to a direct blow. The athlete’s foot is planted and that leg is struck hard. Everyone on the field will hear the snap. On rare occasion the tibia will break if the athlete lands wrong on their leg while their body is twisting.
Types of tibia fractures
Tibia fractures can occur anywhere along your shin bone. If they occur in the middle we call that a mid shaft tibia fracture. If they occur near the top we call them proximal tibia fractures- or tibial plateau fractures. Fractures which occur near the ankle are called distal tibial fractures. The location of the tibia fracture is important. The location will determine what treatment is necessary, and it will significantly impact whether or not the athlete might return to sports. Any fracture that involves the knee joint (tibial plateau) or ankle (distal tibial fracture) can introduce the risk of arthritis as well. This post will focus on mid shaft fractures.
Mid-shaft tibia fractures
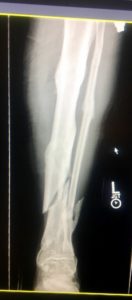
Treatment of a broken tibia
The treatment of a tibia fracture is determined by the type of fracture seen on the X-ray. A fracture which has not displaced, and the two ends are right next to each other can often times be managed in a cast. In a displaced mid shaft fracture we will usually place a rod down the center of the broken tibia to hold the bones in place until the fracture heals.
The athlete with a tibia fracture should be closely examined and monitored. Careful attention should determine if there is a hole in the skin near the fracture. If a hole or cut is found then the fracture is considered “open.” An open fracture requires urgent surgery to clean out the fracture site. This will minimize the risk of developing an infection.
The muscles surrounding the broken tibia will usually swell. In rare instances, they swell too much due to the bleeding from the bone, and a compartment syndrome can develop. In a compartment syndrome the pressure in the muscle is too high and it will not allow blood flow into the muscle or leg. This is a surgical emergency. If we do not release the pressure the muscles and nerves in the leg can die.
Open fractures and compartment syndromes are rare… but can have devastating long lasting effects if they are not identified and managed.
Most tibia fractures treated in a cast or fixed with a rod down the center of the bone will heal. Most displaced tibia fractures will be treated with a titanium rod which is placed inside the bone from the knee to the ankle. It acts as an internal splint to allow the fracture to heal. By stabilizing the tibia fracture, most athletes will be able to start their rehab program very rapidly. The earlier you start your knee and ankle motion and strengthening after the injury, the shorter your recovery can be
Only a small number of tibia fractures will not heal properly. Proper nutrition and at least 8 hours of sleep every night are important. Keeping the leg elevated at rest helps to minimize the swelling after surgery and during the early healing process. There is a question about whether or not NSAIDs or anti-inflammatories affect the healing of tibia fractures. Unless absolutely necessary it is likely best to avoid them.
After the X-rays show that the broken tibia has healed enough to allow weight bearing the athlete will enter into a more intense rehabilitation program. It will take many months to gain back the strength and agility lost during convalescence. Many athletes who had a mid shaft tibia fracture will be able to make a successful return to sports. Some studies show that the time to return to sports may be shorter in the group treated with surgery. Studies in soccer players show that the recovery from a broken tibia can take upwards of 40 weeks.